So I was curious about Prow...
August 09, 2020 -Prow is a CI/CD system used in the Kubernetes repositories. I know it for the ChatOps feature which I found very cool and fun. I decided to give it a try myself and see it in action.
Prerequisites
- A working Kubernetes cluster with internet access
- A GCP account
- A GitHub account
Installation
Prow can be found in Kubernetes' test-infra repository (here). The first thing to do is to clone the repo:
git clone https://github.com/kubernetes/test-infra.git
After that we need to set up an access to GitHub for Prow by creating an access token. The required scope are as follows.
repo:status
public_repo
Next, we need to create two secrets to be used by Prow. One is hmac-token that's going to be used to validate webhooks
openssl rand -hex 20 > hmac-token
kubetl create secret generic hmac-token --from-file=hmac=./hmac-token
And the other is the github-token for the bot account
echo 'insert-github-token-here' > github-token
kubetl create secret generic github-token --from-file=token=./github-token
Next, we're going to update the sample manifest that we're going to use. There are two sample manifests, one with minio as blog storage (starter-s3.yaml) and the other one that uses GCS (starter-gcs.yaml). I decided to use the one with GCS.
With both sample manifests there are things that we need to adjust, those are:
- GitHub token, replace
<<insert-token-here>> - hmac token, replace
<< insert-hmac-token-here >> - domain, replace
<< your-domain.com >> - GitHub organization, replace
<< your_github_org >> - Prow artifacts bucket, replace
gs://bucket-name - Tide's GCS bucket, replace
gs://tide/ - Statusreconciler's GCS bucket, replace
gs://status-reconciler/
Then we need to provide the buckets and a service account to be used by Prow:
$ gcloud iam service-accounts create prow-gcs-publisher
$ identifier="$(gcloud iam service-accounts list --filter 'name:prow-gcs-publisher' --format 'value(email)')"
$ gsutil mb gs://prow-artifacts-bucket-name/
$ gsutil mb gs://tide-bucket-name/
$ gsutil mb gs://status-reconciler-bucket-name/
$ gsutil iam ch allUsers:objectViewer gs://prow-artifacts-bucket-name
$ gsutil iam ch allUsers:objectViewer gs://tide-bucket-name
$ gsutil iam ch allUsers:objectViewer gs://status-reconciler-bucket-name
$ gsutil iam ch "serviceAccount:${identifier}:objectAdmin" gs://prow-artifacts
$ gsutil iam ch "serviceAccount:${identifier}:objectAdmin" gs://tide-bucket-name
$ gsutil iam ch "serviceAccount:${identifier}:objectAdmin" gs://status-reconciler-bucket-name
$ gcloud iam service-accounts keys create --iam-account "${identifier}" service-account.json
$ kubectl -n test-pods create secret generic gcs-credentials --from-file=service-account.json
$ kubectl -n prow create secret generic gcs-credentials --from-file=service-account.json
Next is adding Prow components to the cluster:
kubectl apply -f config/prow/cluster/starter-gcs.yaml
If things goes well we should be able to our external address.
kubectl get -n prow ingress prow
NAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
prow <none> prow.<<yourdomain.com>> an.ip.addr.ess 80, 443 22d
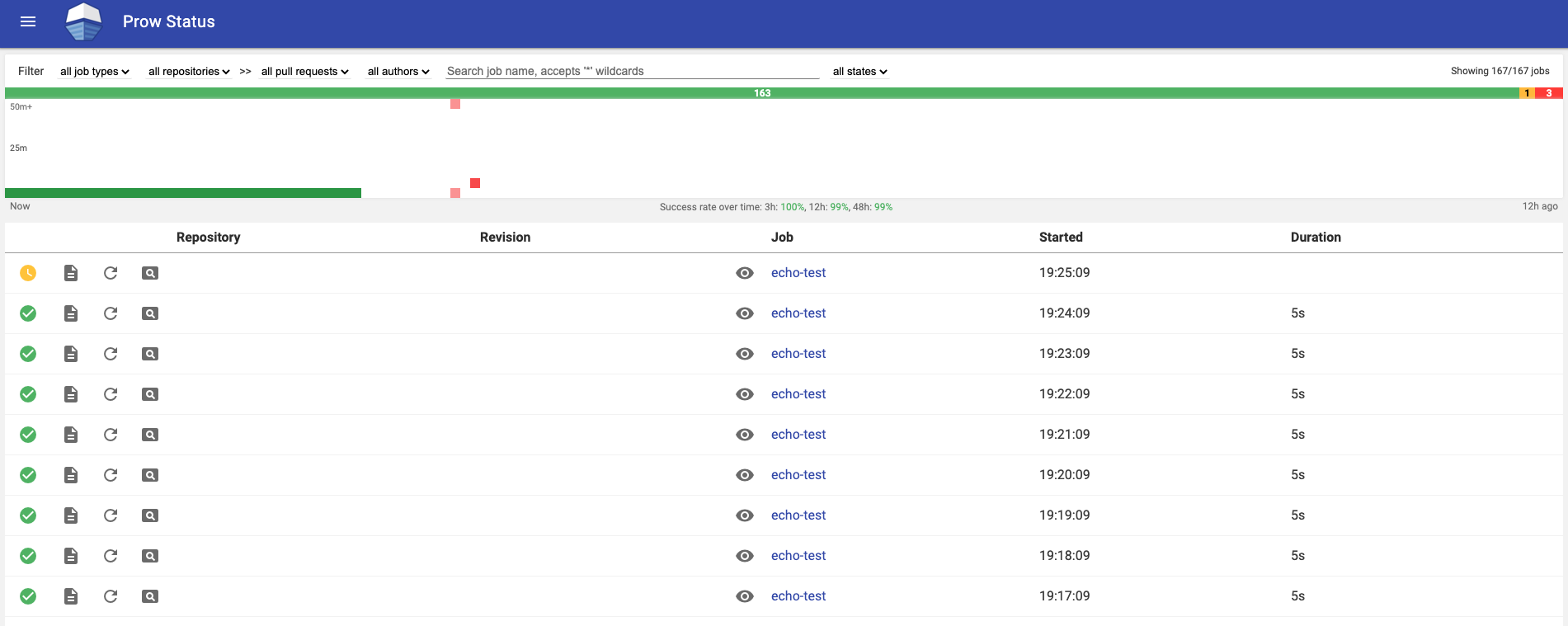
Once we get the address we can go to the address to see Prow's deck. We should see that there's an "echo-test" job, if it is completed there'd be a green check-mark next to it which means Prow is ready to serve.
Next thing we need to do is to add the webhook to GitHub:
- Go to repo and click
Settings -> Webhooks, and clickAdd webhook. - Use the address we get before as the
Payload URL, it should be something like thishttp://an.ip.addr.ess/hook - Change the
Content typetoapplication/json - Use the
hmac-tokenwe generated before as theSecret - Change the trigger to
Send me everything - Click
Add webhook
We should be all set with that.
Usage
Didn't I say that Prow is known for ChatOps, did I? Let's take a look into that. Create a new PR in the repo that's set up before, and try using the commands /meow or /woof to send some furballs to our PR.
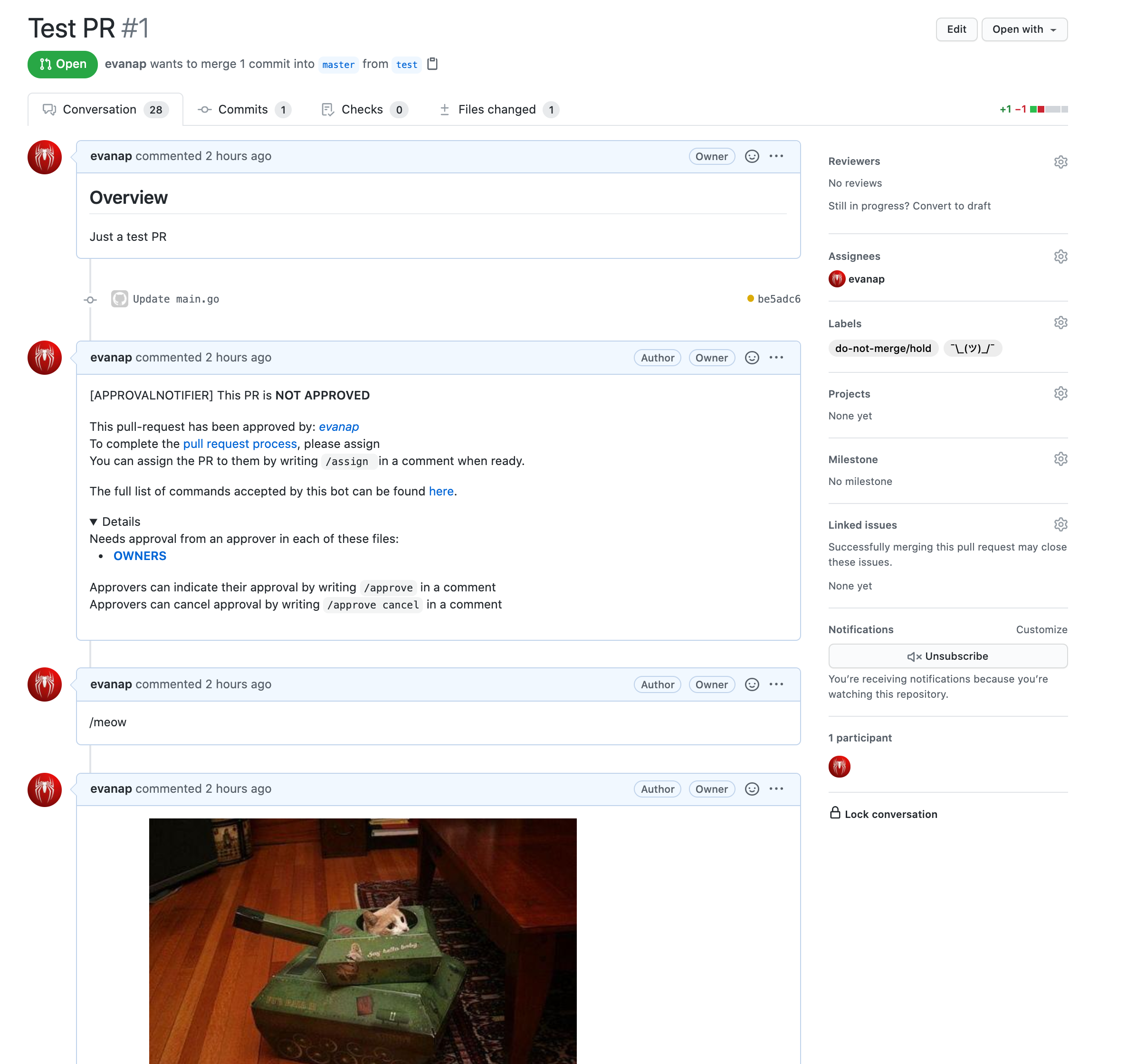
Cool, right? There's more to that. We can see the list of plugins available for Prow by visiting our Prow's plugins catalog.
http://prow.<< your-domain.com >>/plugins
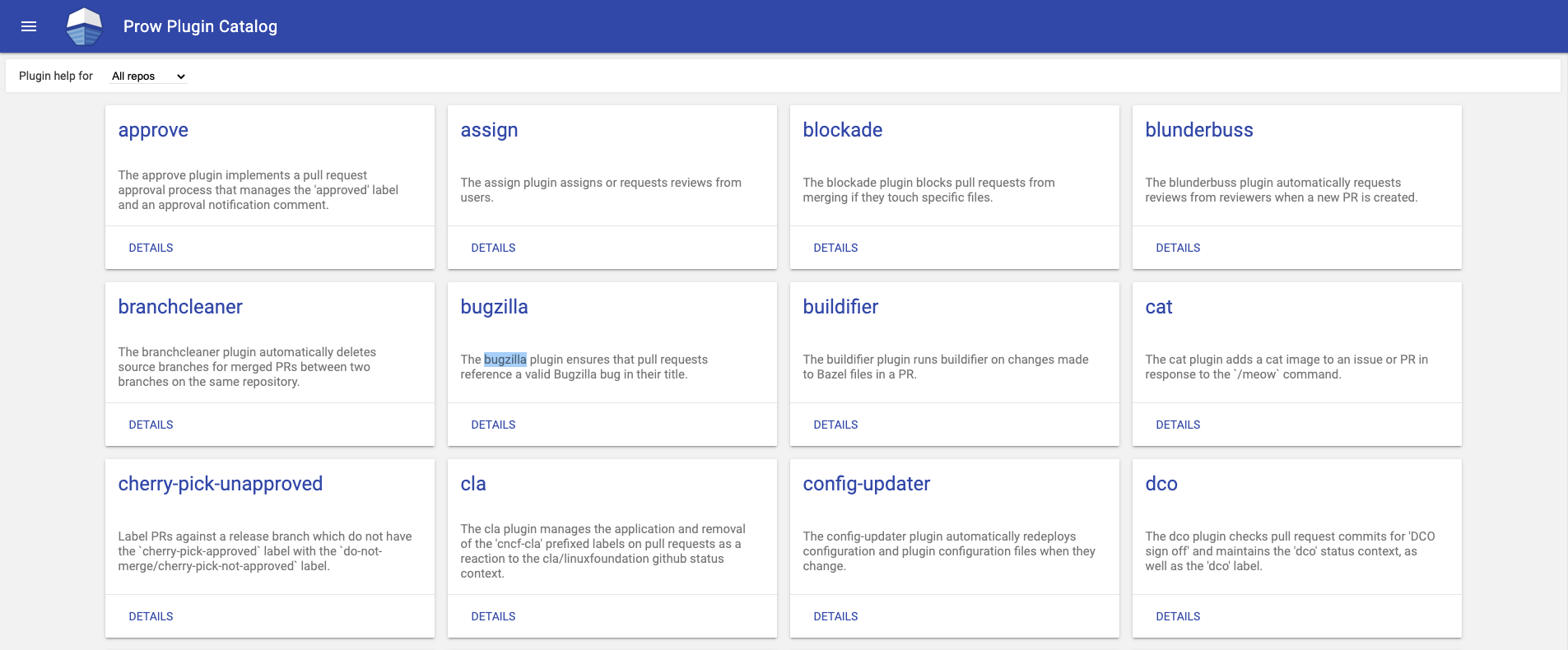
To add more plugins or remove unused plugins, simply edit the prow ConfigMap and add or remove the plugins.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
namespace: prow
name: plugins
data:
plugins.yaml: |
plugins:
evanap/hello:
- approve
- assign
- blunderbuss
- cat
- dog
- help
- heart
- hold
- label
- goose # honks the PR
- override
- shrug
- owners-label
- lifecycle
- lgtm
- trigger
- verify-owners
- wip
- yuks
It's not the easiest CI/CD platform to set up, but once it's up and running it's all cool and easy, plus the plugins feature is a nice thing to add more functions to the platform. And we get to use ChatOps, which is nice.
